VOO vs VUAA: Which ETF is Right for You?
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have become increasingly popular among investors seeking exposure to major market indices. Two prominent ETFs tracking the S&P 500 index are the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) and the Vanguard S&P 500 UCITS ETF (VUAA). While both aim to replicate the performance of the S&P 500, there are important differences investors should consider. The most significant difference lies in their geographic availability and regulatory framework.
Comparing VOO and VUAA: Key Differences to Consider
- Geographic Availability and Regulatory Framework: VOO is primarily available to U.S. investors and is listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). VUAA, on the other hand, is listed on European exchanges like Frankfurt and London Stock Exchange and is structured as a UCITS (Undertakings for Collective Investment in Transferable Securities) fund, making it accessible to European investors and compliant with European regulatory standards.
- Expense Ratio: VOO has an expense ratio of 0.03%, while VUAA has a slightly higher expense ratio of 0.07%. This difference, though small, can impact long-term returns, especially for larger investment portfolios.
- Dividend Treatment: VOO typically distributes dividends quarterly. VUAA is an accumulating ETF. This means that dividends are not distributed to investors but are automatically reinvested.
- Trading Currency: VOO is traded in U.S. dollars, while VUAA is available in multiple currencies, including euros and British pounds, depending on the exchange.
- Fund Size and Liquidity: VOO, being older and more established, generally has a larger asset base and higher trading volumes, potentially offering better liquidity for large trades. VOO was listed in 2010 while VUAA was only started in 2019.
Performance Analysis: Subtle differences in long term performance
Both ETFs aim to track the S&P 500 index closely, and their performance should be very similar before accounting for expenses. However, there are still some subtle differences that can be illustrated using our ETF comparison report generated using our online tool PortfolioMetrics, which analyzes the performance of these two ETFs over a 1 year period.
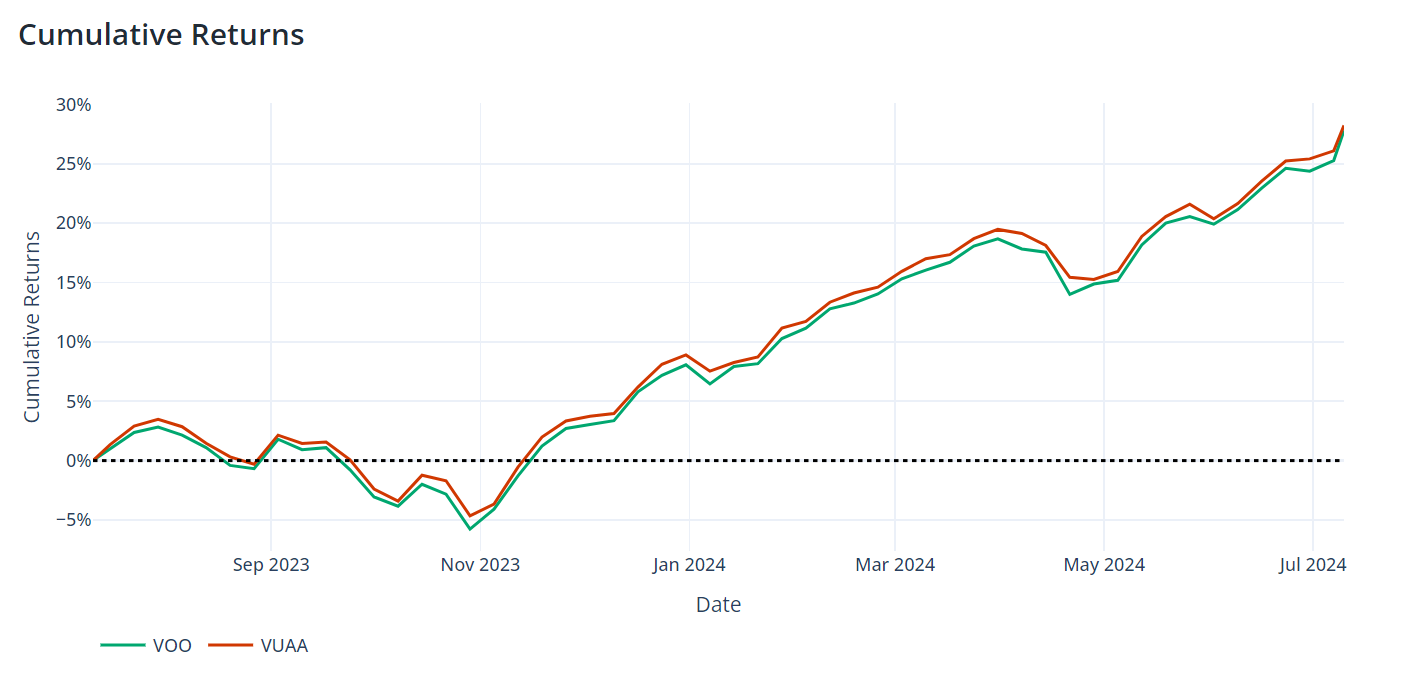
Over the one-year period shown, both VOO and VUAA have demonstrated strong positive returns, with VUAA slightly outperforming VOO. The illustration indicates that both ETFs experienced similar trends, including a dip around November 2023 followed by a steady climb. By July 2024, VUAA showed a cumulative return of approximately 28%, while VOO was close behind at about 26%. The performance difference is relatively small, with VUAA maintaining a slight edge throughout most of the period. This minimal divergence suggests that both ETFs are effectively tracking their underlying index, with the slight outperformance of VUAA possibly attributed to its dividend reinvestment strategy or minor differences in tracking methodology. Overall, both ETFs have provided robust returns for investors over this one-year timeframe.
Performance Discrepancy: A Closer Look
An intriguing question arises when comparing the performance of VOO and VUAA over different time horizons: Despite VUAA being an accumulating ETF that reinvests dividends, some investors have observed that its performance appears lower than that of VOO, which pays out dividends, at least for certain time periods.
Theoretically, an accumulating ETF like VUAA should show slightly better performance over time due to the compounding effect of reinvested dividends. However, several factors could potentially explain this discrepancy:
- Currency Effects: VUAA is traded in euros or pounds, while VOO is in US dollars. Currency fluctuations can impact the apparent performance when converted to a common currency.
- Tracking Difference: Both ETFs aim to track the S&P 500, but small differences in their tracking methodologies or efficiency could lead to slight variations in performance.
- Expense Ratio: VUAA's slightly higher expense ratio (0.07% vs 0.03% for VOO) could contribute to a small performance difference over time.
- Trading Hours and Pricing: Different trading hours between US and European markets might affect how quickly each ETF reflects market changes, potentially leading to short-term discrepancies.
- Tax Considerations: The way dividends are treated for tax purposes in different jurisdictions could affect the net performance of each fund.
It's crucial to note that without a comprehensive analysis across various time frames and accounting for multiple factors, definitively explaining any perceived performance gap is challenging. When comparing these ETFs, investors should consider their individual circumstances, including tax situations and the currency they'll ultimately need their returns in. For a thorough understanding of performance dynamics, compare the ETFs over different periods, focus on total return (including reinvested dividends for VOO) rather than just price movements, account for currency conversions if comparing in a single currency, and consult the ETF providers' official performance data and tracking difference reports.
When to Use VOO or VUAA: Scenarios and Preferences
- U.S. Investors: VOO is likely the preferred choice due to its lower expense ratio and ease of access through U.S. brokerages.
- European Investors: VUAA is the more suitable and for some to only available option due to its UCITS compliance and availability on European exchanges.
- Currency Preference: Investors who prefer to trade in euros or pounds may find VUAA more convenient.
- Expense-sensitive Investors: Those prioritizing the lowest possible fees might lean towards VOO, given its lower expense ratio.
- Dividend Preferences: Investors can choose between VOO's quarterly distributions or VUAA's accumulating character.
Conclusion: Making the right choice between VOO and VUAA
While VOO and VUAA both offer exposure to the S&P 500 index, the choice between them largely depends on an investor's geographic location, regulatory considerations, and specific preferences regarding expenses and dividend treatment. U.S.-based investors may find VOO more suitable, while European investors might prefer VUAA due to its UCITS status and multi-currency trading options.
By understanding these key differences, investors can make informed decisions aligning with their investment goals and circumstances. Remember to consider factors such as tax implications, currency exchange rates, and overall portfolio strategy when choosing between these ETFs. Visit our PortfolioMetrics dashboard to analyze the performance and risks of your investment portfolio.
[Note: This article provides general information and should not be considered as financial advice. Always conduct thorough research or consult with a financial professional before making investment decisions.]