
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have become increasingly popular investment vehicles, offering investors diversified exposure to various markets and sectors. Among the most well-known ETFs are the Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ) and the Invesco NASDAQ 100 ETF (QQQM), both of which track the performance of the Nasdaq-100 Index, which consists of the 100 largest non-financial companies listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market. This index is heavily weighted toward technology companies, with giants like Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, and Google (Alphabet) making up a significant portion of its holdings. While these two ETFs share similarities, they also have distinct differences that investors should understand before making investment decisions.
Comparison: QQQ vs. QQQM
The QQQ, launched in 1999, is one of the oldest and most widely traded ETFs in the market. The QQQM is a newer entrant, having been introduced in 2020. Both ETFs track the same index, Nasdaq-100 Index. However, there's a key difference between the two ETFs: the QQQM is structured as a traditional index fund, while the QQQ is structured as a unit investment trust (UIT). This structural difference has implications for taxes, rebalancing, and trading flexibility.
Key differences:
-
Expense Ratio: The QQQM has a lower expense ratio of 0.15%, compared to the QQQ's 0.20%. While the difference may seem small, it can significantly impact long-term returns, especially for larger investment portfolios.
-
Trading Flexibility: The QQQM, being a traditional index fund, offers more trading flexibility compared to the QQQ. Investors can purchase or redeem shares directly from the fund, which can be advantageous for large institutional investors or those seeking tax efficiency.
-
Tax Efficiency: Due to its structure as a UIT, the QQQ can be less tax-efficient than the QQQM, as it must distribute capital gains annually, even if investors don't sell their shares.
Expense Ratio Analysis
While both the QQQ and QQQM offer exposure to the same Nasdaq-100 Index, their expense ratios can have a significant impact on long-term returns. To illustrate this, we can refer to an ETF comparison report generated using our online tool PortfolioMetrics, which analyzed the performance of these two ETFs over the period from 14/10/2020 to 04/03/2024.
The report reveals that the QQQM outperformed the QQQ in terms of cumulative returns (51.0% vs 50.8%) and compound annual growth rate (CAGR) (8.8% vs 8.7%). This performance advantage can be attributed to the QQQM's lower expense ratio, which allows more of the fund's returns to be passed on to investors.
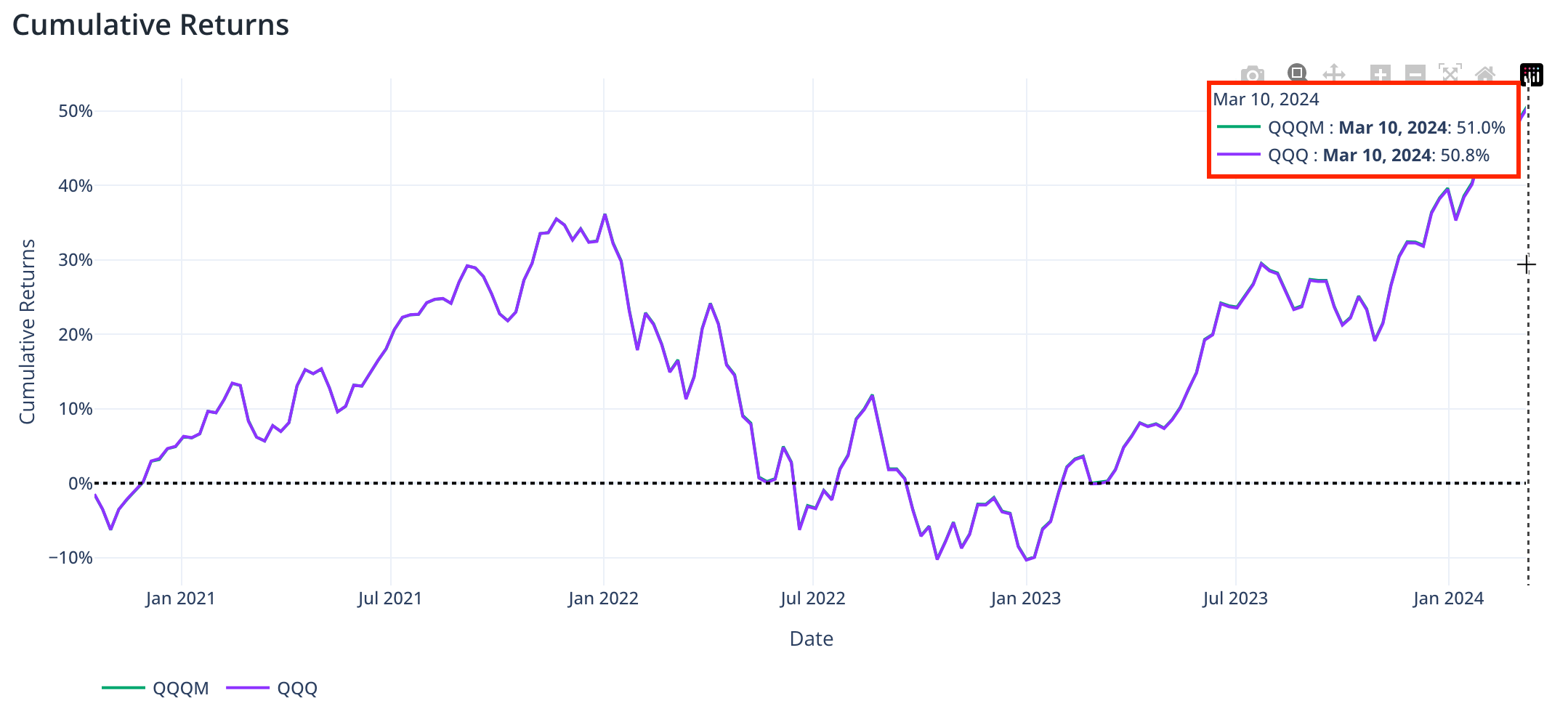
Notice, the difference in the figure between QQQ and QQQM return curves is so tiny that the QQQM curve (green) is not visible as it is overflown with the QQQ curve (purple).
Over longer investment horizons, the compounding effect of lower expenses can lead to significant differences in overall returns. Therefore, cost-conscious investors looking to maximize their returns from the Nasdaq-100 Index may find the QQQM a more attractive option compared to the QQQ, especially for larger investment portfolios.
It's important to note that while expense ratios are a crucial factor in evaluating ETFs, investors should also consider other factors such as trading flexibility, tax efficiency, and their investment goals before making an informed decision.
When to Use QQQ or QQQM
The choice between QQQ and QQQM ultimately depends on an investor's preferences and investment goals. Here are some scenarios where one ETF may be more suitable than the other:
-
Long-term investors: For long-term investors seeking exposure to the Nasdaq-100 Index, the QQQM may be a better choice due to its lower expense ratio and potentially greater tax efficiency.
-
Active traders: Active traders or those seeking intraday trading flexibility may prefer the QQQ, as it is more liquid and trades like a stock throughout the day.
-
Tax-sensitive investors: Investors concerned about minimizing taxable events may find the QQQM more appealing due to its potential for greater tax efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both the QQQ and QQQM offer exposure to the Nasdaq-100 Index, but they differ in structure, expense ratios, trading flexibility, and tax efficiency. Investors should carefully evaluate their investment goals, trading preferences, and tax considerations before deciding which ETF better suits their needs.